Have you ever noticed how some printed boxes or brochures have a smooth, shiny surface that resists fingerprints and scratches? That protective layer is called a coating and one of the most popular types used today is aqueous coating (AQ). It’s an eco-friendly, water-based finish that not only keeps your prints safe but also gives them a professional look.
In the printing and packaging industries, aqueous coating is widely used for its bright and reflective appearance. This type of coating is applied to the printed sheet to give it a smooth, shiny surface that enhances color depth and visual appeal. In addition to offering protection against scratches, fingerprints, and scuffs, aqueous coating adds a polished finish that makes the final product look more vibrant and attractive.
What is Aqueous Coating in Printing?
Aqueous coating is a form of varnish that is clear and based on water. It is applied to a printed object while the printing process is being carried out. In the printing and packaging industries, aqueous coating is often used as the standard coating process because it dries rapidly, is resistant to fingerprints, is helpful to the environment, and facilitates the creation of unique package designs.
How Aqueous Coating Works
Aqueous coatings are made of water mixed with polymers and resins that form a thin, protective film once dried. When applied, the water evaporates quickly, leaving behind a clear layer that seals the print surface. This coating bonds well with paper or cardboard, preventing ink from rubbing off while giving the product a polished finish.

Types of Aqueous Coatings

1- Gloss Coating
Gloss coating is one of the most popular finishes. It creates a shiny and reflective surface that makes colors look rich and vibrant. Along with enhancing visual appeal, it also protects against scratches, fingerprints, and scuffs — giving the final product a bright and professional look. Read our detailed post on Gloss Aqueous Coating to learn when it’s the best choice and how it enhances your packaging.

2- Matte Coating
Matte coating offers a smooth, non-shiny surface that gives printed materials a soft and elegant appearance. Unlike gloss, it reduces glare and provides a clean, modern look. This coating works well for premium or minimalist designs that require a subtle and refined finish. Discover how matte aqueous coating creates a flat, non-reflective surface and adds a touch of elegance to prints in our detailed post what is matte aqueous coating a complete guide.

3- Satin Coating
Satin coating provides a balanced look between gloss and matte. It has a slight sheen without being overly reflective. This type of coating protects prints from smudges and scratches while maintaining a natural and professional appearance — ideal for packaging or printed materials that need a soft shine. Learn more about how satin aqueous coating gives printed materials a smooth, soft shine and balanced finish in our full guide on what is satin aqueous coating?
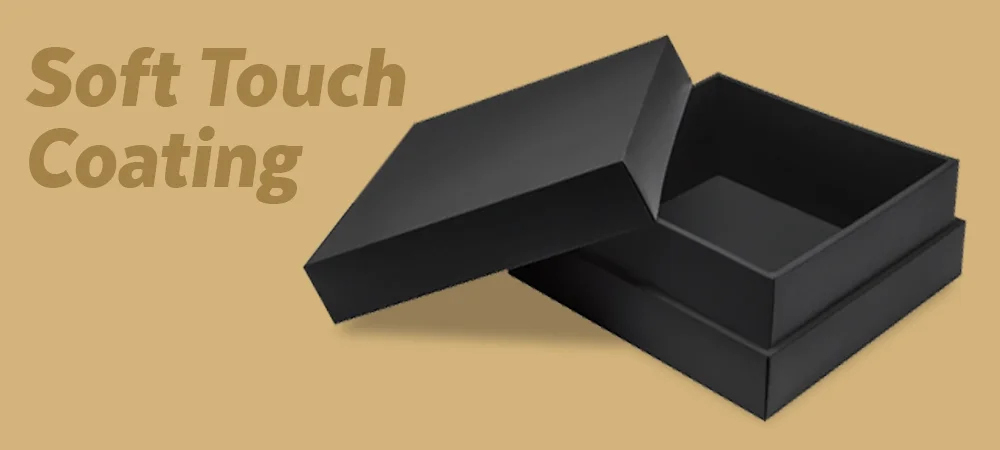

4- Soft Touch Coating
Soft touch coating gives packaging a smooth, velvety texture that feels luxurious to the touch. It not only enhances the appearance but also improves the tactile experience. This coating is often used on high-end boxes, brochures, and business cards where quality and feel matter most. if you still corious about how its work and when use it here is complete guide about what is soft touch aqueous coating?

5- Dry Erase Coating
Dry erase coating provides a glossy finish similar to lamination but at a lower cost. It allows the surface to be written on and wiped clean, making it practical for reusable printed materials. Though not as durable as full gloss, it offers an excellent combination of function, shine, and affordability.

Benefits of Aqueous Coating
Aqueous coating is widely used in the printing industry for several reasons. It is a water-based coating that offers multiple benefits, making it a popular choice over other types of coatings, like UV or solvent-based coatings.
Environmental Benefits
The main reason why aqueous coatings are the best choice is because it is water based coating. Water-based coatings have less volatile organic compounds (VOCs) than any other types of coatings. VOCs are dangerous for both human health and environment, that's why using a low- or no-VOC aqueous coating is the top priority. This makes aqueous coatings a safer choice for workers and the environment.
Cost-Effective
Aqueous coatings are often less expensive than other types of coatings, such as UV coatings, because they do not require expensive curing equipment. Aqueous coatings dry faster, resulting in reduced manufacturing times and lower costs.
Durability and Protection
Aqueous coatings form a protective layer, making printed materials more resistant to wear and tear. It protects the print from scratches, smearing, fingerprints, and dampness. It also extends the life of printed goods and makes them more durable.
Aesthetic Improvement
Aqueous coatings can enhance the appearance of printed items. Depending on the type of aqueous coating used, it can produce a glossy or matte surface, increasing the visual appeal of the material. This is especially relevant for items such as brochures, periodicals, and packaging.
Limitations of Aqueous Coating
While aqueous coating has many benefits, it’s not perfect for every project.
-
It doesn’t provide as much water or chemical resistance as UV coatings.
-
It’s not suitable for spot or textured effects, since it usually covers the entire surface.
-
On very thin or uncoated papers, too much coating can cause curling or wrinkling.
-
Heavy ink coverage or metallic inks may lead to slight color shifts or dulling.
Understanding these limits helps you decide when aqueous coating is the best fit and when other options like UV or lamination might be better.
Paper Compatibility and Printing Tips
Aqueous coating works best on coated papers and cardstocks that are smooth and non-porous. Avoid using it on very rough or absorbent papers, which can soak up the coating unevenly.
-
Make sure ink is completely dry before applying the coating.
-
Avoid using metallic or oil-based inks that repel water.
-
If your design has large dark areas, test first to prevent “burnishing” or dull spots.
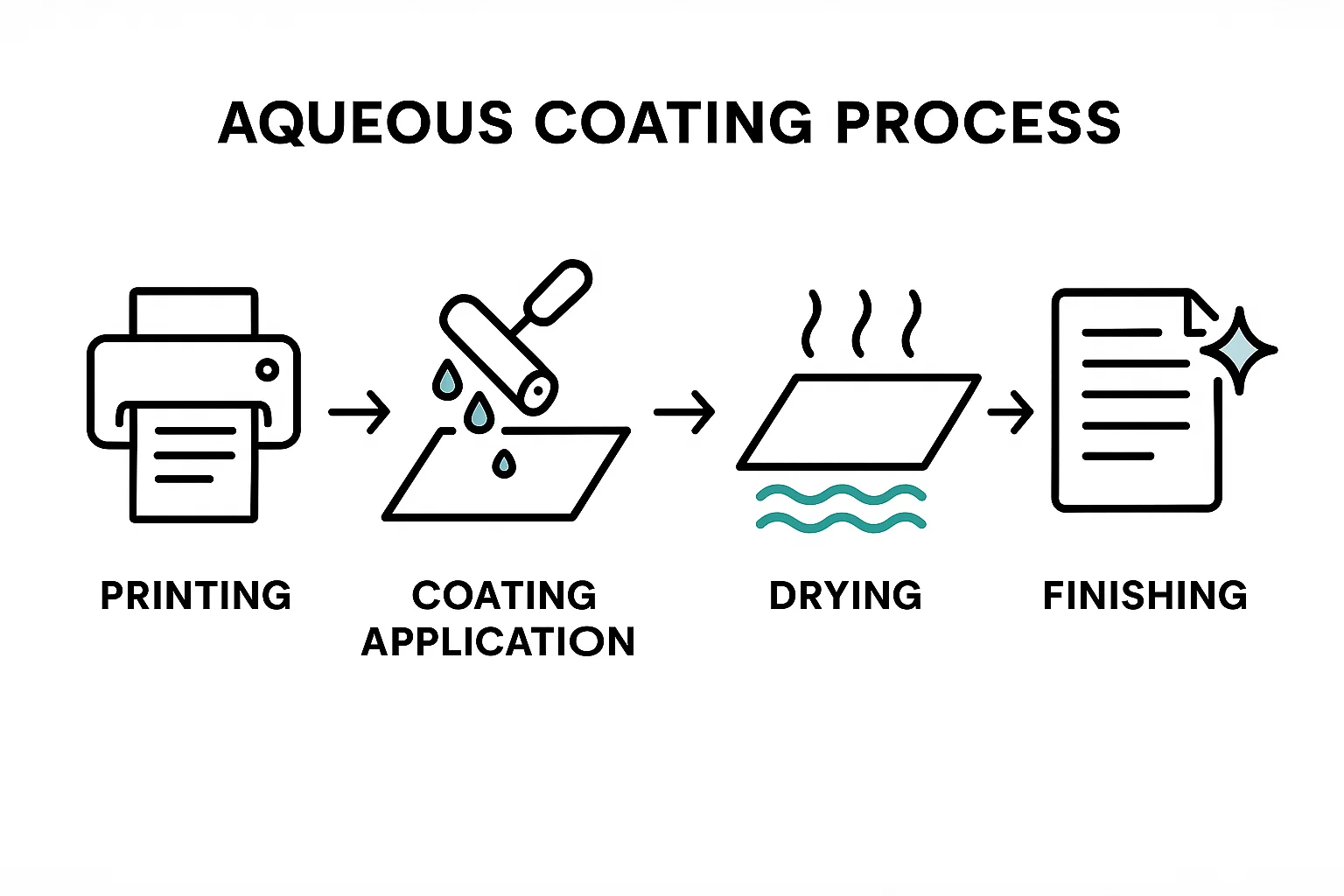
Process of Aqueous Coating
The aqueous coating method includes putting a thin layer of water-based coating to a printed surface. This protective layer is added after the printing process is completed, providing durability and aesthetic benefits. The process is simple and efficient, ensuring high-quality results.
The aqueous coating process consists of several key steps, each contributing to the final result. Below are the primary stages of the aqueous coating process:
1. Printing
The first step in the aqueous coating process is the printing itself. In this stage, the design is printed onto the surface of the material, typically paper, cardboard, or other substrates. Different types of printing techniques like offset printing, digital printing, or flexographic printing are commonly used. After printing, the material will often appear dull or unfinished, that's why the coating is applied to give it a more polished and protected look.
2. Coating Application
Once the printed material has dried (if necessary), the aqueous coating is applied. This is typically done on a coating machine or as part of a printing press. There are two main methods for applying the aqueous coating:
- Spraying: The coating is sprayed evenly across the printed surface.
- Roller Application: A roller is used to spread the coating across the material in a smooth, even layer.
The coating is applied as a thin layer, enough to protect the print but not too thick to cause uneven drying or a sticky finish. The type of coating applied will depend on the desired effect (glossy or matte).
Inline vs Offline Coating
In modern printing presses, aqueous coating is often applied inline, meaning it’s added immediately after the ink is printed — saving time and ensuring smooth results. However, for specialty jobs, printers may use offline coating, where the sheets are coated in a separate machine after printing.
Flood vs Spot Coating
Aqueous coatings are usually flood coatings, which means the entire surface is covered. Unlike UV coatings, spot applications (where only certain areas are coated) are less common but can be achieved with specialized equipment.
3. Drying
After the aqueous coating is applied, it needs to dry. The drying process is relatively fast compared to other coating types. The coating typically dries through evaporation, which means the water content evaporates into the air. Some machines use heat or air blowers to speed up the drying process. Since aqueous coatings dry quickly, they help reduce production time and allow for faster processing. This is important in high-volume printing environments where time is a critical factor.
4. Finishing
Once the coating has dried, the final finishing steps begin. This can include cutting the material into its final shape, trimming the edges, or folding it into a specific form. In some cases, additional steps like embossing, die-cutting, or laminating may be performed.
The final material is now ready for distribution or further processing. Whether it’s a book cover, a brochure, or packaging material, the aqueous coating has ensured that the printed piece is visually appealing and protected against wear and tear.
Use of Aqueous Coating in Printing & Packaging?
Aqueous coating is widely used across various industries, especially in areas that require printed materials with high durability and visual appeal. Some of the most common applications of aqueous coatings include:
1. Packaging
Aqueous coatings are commonly used in custom packaging, especially for products like food, cosmetics, and electronics. Packaging materials benefit from the coating’s protective layer, which helps keep the product safe during transportation and handling. It also improves the overall appearance of the packaging, making it more attractive to consumers.
2. Magazines and Brochures
Printed marketing materials, such as magazines, brochures, and catalogs, often have an aqueous coating applied to give them a glossy or matte finish. This improves the visual appeal and ensures that the prints stay in good condition over time. Aqueous coating also helps prevent ink smudging or fading, keeping the printed content clear and vibrant.
3. Books and Publications
Books, especially hardcover books, benefit from aqueous coatings. The coating helps protect the cover from scratches, fingerprints, and moisture, ensuring the book remains in good condition for longer periods. It can also improve the tactile feel of the book cover, giving it a more professional and polished finish.
4. Business Cards and Stationery
Business cards, letterheads, and other office stationery often have aqueous coating applied to give them a high-quality appearance. This coating helps protect the printed materials from damage while making them look more polished and professional.
5. Labels and Tags
Product labels and tags, which are often exposed to harsh conditions, can benefit from aqueous coating. The coating helps protect the print from smudging, fading, or getting damaged by moisture, making labels more durable in challenging environments.
Quick Comparison Between Aqueous Coating vs UV Coating vs Varnish vs Lamination
Here’s a quick comparison between aqueous coating, UV coating, varnish, and lamination to help you decide what fits best.
| Difference Point | Aqueous Coating | UV Coating | Varnish | Lamination |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material Base | Water-based coating | Liquid polymer cured with UV light | Oil or resin-based | Thin plastic film applied over print |
| Finish Look | Smooth, light gloss or matte finish | Very glossy and reflective | Can be gloss, matte, or satin | Glossy or matte, thick layer |
| Durability | Moderate protection from scratches and smudges | Very strong and long-lasting protection | Basic protection level | Excellent protection and water resistance |
| Drying Method | Air or heat dried | UV light cured instantly | Air or heat dried | Applied using pressure and heat |
| Eco-Friendliness | Yes, water-based and low VOC | Less eco-friendly | Moderate | Not eco-friendly (plastic layer) |
| Common Uses | Packaging, brochures, flyers | Business cards, magazine covers | Books, posters | Premium boxes, menus, cards |
Future of Aqueous Coatings in Printing
The printing industry continues to improve aqueous coating technology. New formulas offer low-curl coatings for lightweight papers, hybrid matte-soft touch finishes, and anti-microbial coatings for hygiene-sensitive packaging. Some printers are even experimenting with biodegradable AQ coatings, making sustainable packaging even more achievable.
Conclusion
Aqueous coating is one of the most versatile and eco-friendly finishes in the printing world. From glossy magazines to luxury packaging, it adds both protection and beauty without harming the environment. Choosing between aqueous and UV coating depends on your project’s needs whether you want a soft matte touch or a high-shine, durable finish.
At HT Custom Boxes, we offer a full range of coating options and professional design support to bring your packaging ideas to life. Contact us today or request a free quote or to discuss which coating is best for your next project.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is aqueous coating waterproof?
Aqueous coating is water-resistant but not fully waterproof. It protects printed materials from light moisture, spills, and fingerprints, but it’s not suitable for long-term exposure to water.
What is aqueous coating made of?
Aqueous coating is made from a mix of water, polymers, and additives. These materials create a thin protective layer that adds shine or a matte finish and protects the print from scratches and scuffs.
Is aqueous coating food safe?
Yes, aqueous coating is generally considered food safe once it is fully cured. This makes it a common choice for packaging in the food and beverage industry.
Is aqueous coating shiny?
It can be shiny or dull, depending on the type used. Gloss aqueous coating gives a bright, reflective surface, while matte or satin coatings provide a softer look.
Is aqueous coating recyclable?
Yes, aqueous coatings are eco-friendly and recyclable. Since they are water-based and contain very low VOCs, they don’t harm the environment and can be processed with most recycled papers.
 Aminah Zaheer
Aminah Zaheer















.webp)





































